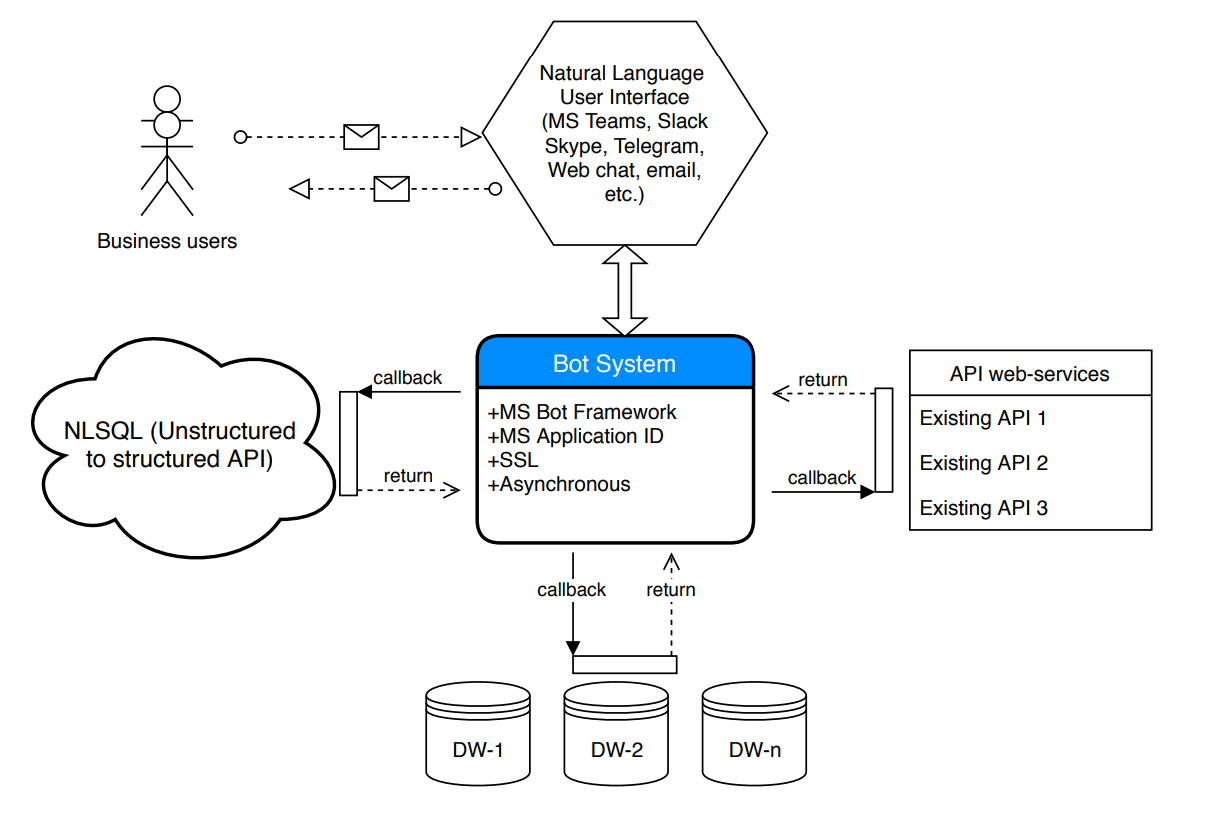
What is RPA Architecture? A revolution in business process automation
To remove tedious tasks, more CIOs shift to robotic process automation, allowing corporate employees to focus on higher-value work. However RPA needs careful design, preparation, and governance if the company is to be sustained, experts say.
To streamline business operations and reduce costs, more CIOs are shifting to an emerging technology practice called robotic process automation (RPA). Businesses can automate routine business processes based on rules with RPA, allowing business users to spend more time serving customers or other higher-value jobs. Others see RPA as a stopover on the road to intelligent automation (IA) by machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) methods that can be trained to make decisions on potential outputs.
What is robotic process automation?
RPA is an application of technology to automate business processes, controlled by business logic and organized inputs. A business can configure software or a "robot" using RPA tools to capture and interpret transaction processing applications, manipulate data, activate responses, and interact with other digital systems. RPA scenarios range from something as simple as automatically generating an email response to deploying thousands of bots, each programmed to automate jobs in an ERP system.
COOs working for financial services companies were at the forefront of RPA adoption, identifying ways to use software to facilitate business processes without increasing headcount or costs.
What are RPA's advantages?
RPA provides the ability to reduce personnel costs and human error to organizations. Bots are usually low-cost and easy to deploy, requiring no incorporation of custom software or deep systems. These attributes are critical when companies drive success without excessive staff spending or friction.
Companies can also overwhelm their automation efforts by combining RPA with cognitive technology such as ML, speech recognition, and natural language processing, automating higher-order tasks that previously required human perceptual and decision capabilities. Such RPA implementations are part of a value chain known as intelligent automation (IA), where up to 15 to 20 steps can be automated.
What are RPA's pitfalls?
RPA is not for any company. RPA has the ability to eliminate jobs, as with any automation technology, which presents CIOs with talent management challenges. Even if CIOs manage the conundrum of human capital, more often than not, RPA implementations fail. It took a lot longer to install thousands of bots and is more complex and expensive than most organizations thought it would be. The platforms on which bots interact frequently change, and not always configure the necessary flexibility into the bot. In addition, a new regulation requiring minor changes to an application form could throw off months of work on a bot near completion in the back office.